Understanding LPG Reticulated Systems in Bangladesh: A Guide According to Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004 and NFPA 58
In Bangladesh, the demand for safe, reliable, and efficient fuel distribution systems has grown substantially, especially in residential and commercial high-rise buildings. The Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Reticulated System has emerged as a practical solution, offering centralized gas supply with improved safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
This blog provides an in-depth look at LPG reticulated systems based on Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004 and international best practices, specifically NFPA 58 (Liquefied Petroleum Gas Code). It aims to help engineers, developers, facility managers, and end-users understand the system design, safety standards, legal obligations, and benefits.
What is an LPG Reticulated System?
A reticulated LPG system is a centralized gas distribution network installed within a building complex or housing society. Instead of using individual LPG cylinders for each kitchen or unit, a common gas bank (cylinder manifold or bulk storage tank) is set up. From this central point, LPG is distributed through a network of pipelines to multiple consumers.
Why Bangladesh Needs Reticulated LPG Systems
With increasing urbanization and the popularity of apartment-style living, especially in cities like Dhaka and Chattogram, there is a growing need for:
- Efficient fuel management
- Enhanced safety standards
- Reduced dependence on cylinder replacements
- Lower cost through bulk gas purchases
The LPG reticulated system addresses all of these needs while aligning with government regulations.
Regulatory Framework: Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004
The Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004, issued under the Explosives Act, 1884, regulate the import, storage, distribution, filling, transport, and usage of LPG. It provides legal guidance for:
- Safety requirements
- Installation approvals
- Storage limitations
- Licensing procedures
- Periodic inspections
Some relevant rules from the act that apply to reticulated systems include:
Rule 14: Storage of LPG
- LPG can only be stored in approved cylinders or bulk tanks.
- Cylinders must be stored in well-ventilated, open spaces.
- No open flame, electrical switches, or other sources of ignition within 3 meters.
Rule 20: License Requirements
- Any person or company installing an LPG system must have a valid license from the Department of Explosives (DOE).
- Separate licenses are required for storage, filling, and distribution.
Rule 24: Cylinder Manifold Systems
- Proper labeling and signage must be in place.
- Only approved regulators, piping materials, and fittings should be used.
International Benchmark: NFPA 58 Guidelines
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 58, also known as the LPG Code, is the international standard governing the safe design, installation, and operation of LPG systems. Though not legally binding in Bangladesh, it is widely followed for ensuring best practices.
NFPA 58 provides technical guidance on:
- Cylinder and tank safety
- Pressure relief devices
- Piping design and materials
- Leak detection and shutdown systems
- Fire protection and emergency planning
In Bangladesh, most engineering consultants and contractors follow NFPA 58 along with the LPG Rules 2004 to ensure safety and compliance.
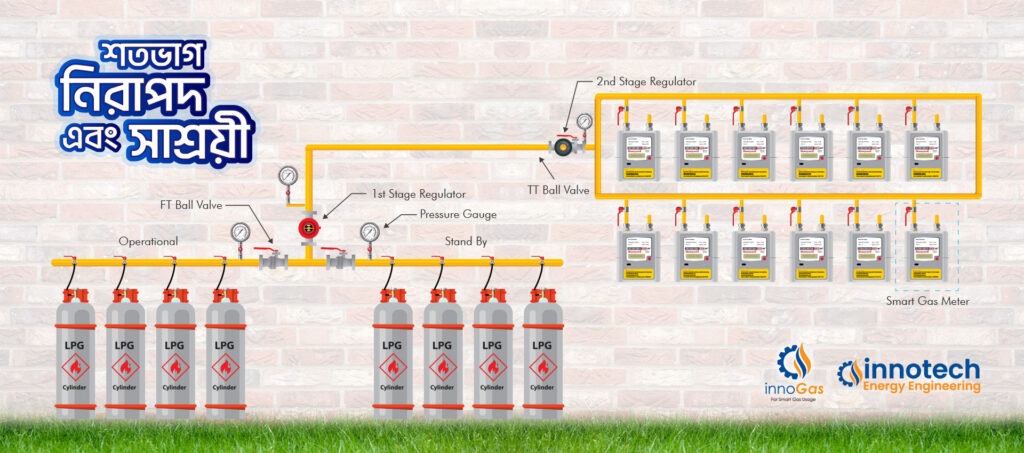
Components of a Reticulated LPG System
A typical LPG reticulated system in a building includes the following components:
1. LPG Source
- Cylinder Bank: Multiple 45 kg or 33 kg cylinders connected in a manifold system.
- Bulk Storage Tank: Underground or above-ground tank with higher capacity (common in commercial/industrial setups).
2. Pressure Regulators
- Two-stage pressure regulation:
- First stage: Reduces cylinder pressure to intermediate level.
- Second stage: Brings pressure to domestic level (~30-35 mbar).
3. Piping Network
- Medium-pressure piping from the gas bank to each floor.
- Low-pressure piping from floor-level regulators to individual kitchens.
4. Shut-off Valves & Isolation Valves
- Essential for emergency shutdown and maintenance.
- Each unit should have an isolation valve for safety.
5. Leak Detection System
- Gas detectors installed in utility areas or kitchens.
- Automatic shut-off valves activated in case of leakage.
6. Meters
- Optional for individual usage tracking and billing (prepaid or postpaid meters).
7. Fire Protection
- Fire extinguishers, signage, and ventilation as per both Bangladesh and NFPA standards.
Design Considerations
When designing a reticulated LPG system, the following factors must be considered:
a. System Sizing
- Number of flats/units
- Consumption rate per unit
- Simultaneous usage factor
- Peak load calculation
b. Material Selection
- Use of seamless carbon steel (SCH 40/80) or copper tubing depending on local standards.
- Brass or forged steel fittings for joints and connections.
c. Pipe Routing
- Avoid electrical ducts or shafts.
- Maintain minimum clearances from electrical lines and water pipelines.
- Outdoor piping should be UV protected and painted (yellow).
d. Ventilation
- Cylinder storage and pipe routing areas must be well ventilated.
- Accumulated LPG vapors (being heavier than air) can cause explosions.
Safety Features and Compliance
To ensure compliance with both Bangladesh Rules 2004 and NFPA 58, the system should include:
- Overpressure protection: Relief valves must be installed at proper points.
- Flame arrestors: To prevent flame backflow from kitchen to manifold.
- Color Coding: Yellow paint for gas lines; red for fire lines.
- Testing & Commissioning: Hydrostatic pressure testing and soap water leak test before handover.
Approval and Licensing Process in Bangladesh
Before installing a reticulated LPG system, the following steps are mandatory:
1. Design Approval
- Submit detailed layout, technical drawings, and bill of materials to the Department of Explosives (DOE).
2. Fire Service Approval
- Seek No Objection Certificate (NOC) from the Fire Service and Civil Defence (FSCD).
3. Installation by Licensed Contractor
- Only DOE-approved contractors can install the system.
4. Final Inspection
- Post-installation inspection by DOE and FSCD.
- Ensure compliance with Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004.
5. License Issuance
- Operating license is issued upon approval.
- Subject to annual renewals and inspections.
Advantages of LPG Reticulated System
✔️ User Convenience
No need for manual cylinder replacement; continuous supply ensures user comfort.
✔️ Safety
Reduced risk of cylinder mishandling, unauthorized cylinder use, or explosion.
✔️ Cost Efficiency
Bulk procurement reduces fuel cost; easy to monitor usage and prevent wastage.
✔️ Real-time Monitoring
Advanced systems allow IoT integration for gas level monitoring and leak alerts.
✔️ Aesthetic and Space Saving
Centralized storage frees up kitchen space in apartments.
Challenges and Solutions
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Complex licensing process | Engage experienced consultants and licensed contractors |
| High upfront installation cost | Recoverable over long-term savings and convenience |
| Lack of public awareness | Conduct safety training and awareness programs |
| Corrosion and leaks in piping systems | Use of corrosion-resistant materials and regular inspection |
Maintenance Guidelines
Regular maintenance is essential for the safety and efficiency of LPG reticulated systems. As per NFPA 58 and best practices:
- Daily: Visual inspection of pressure gauges and detectors.
- Monthly: Leak test at selected joints.
- Annually: Full hydrostatic pressure test and regulator calibration.
- Every 5 Years: Replace pressure regulators and flexible hoses.
Future of Reticulated Systems in Bangladesh
As the demand for clean energy grows, LPG reticulated systems will become more widespread in:
- Residential apartments
- Commercial kitchens
- Educational institutions
- Hospitals and hotels
With proper government regulation, training programs, and strict compliance to Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004 and NFPA 58, reticulated systems can play a major role in ensuring a safe, sustainable, and smart energy future for urban Bangladesh.
Conclusion
The LPG Reticulated System is a smart and safe alternative to conventional cylinder-based gas supply in buildings. When designed and implemented according to Bangladesh LPG Rules 2004 and NFPA 58, it offers numerous benefits in terms of convenience, cost savings, and safety. However, successful implementation requires licensed professionals, strict adherence to regulatory guidelines, and continuous monitoring.

